![]() Installing
the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2 Software
Installing
the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2 Software
![]() Updating
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2
Updating
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2
![]() Removing
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2
Removing
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2
![]() Starting
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2
Starting
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2
![]() Using
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2
Using
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2 (BACS2) is an integrated utility that provides useful information about the Broadcom Gigabit Ethernet adapter that is installed in your computer. BACS2 also enables you to perform detailed tests, diagnostics, and analyses on the adapter, as well as to view and modify property values and view traffic statistics. BACS2 contains three panes:
 |
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2 lists all of the network adapters in your computer and provides the following information (if available) about each adapter:
|
|
|
Vital Sign. At-a-glance information on all of the LAN adapters in your computer.
Resources. Shows the resource settings for the selected adapter.
Hardware. Shows the hardware information for the selected adapter.
Advanced. Shows the available properties and their values for the selected adapter.
Statistics. Provides detailed performance statistics for the selected adapter.
The following tests, diagnostics, and analyses are provided:
Network Test. Confirms network connectivity to a remote station.
Diagnostics. Performs comprehensive diagnostics on Broadcom network adapters.
Cable Analysis. Determines if you have the appropriate length of cable connected.
The BACS2 install file (Setup.exe) is on the installation CD in the BACS folder.
| |
NOTE: Before you begin the installation, close all applications, windows, or dialog boxes. |
To install BACS2
| |
NOTE: Before you begin the update, close all applications, windows, or dialog boxes. |
Follow the same instructions as for Installing the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2 Software.
In Control Panel, click (or double-click) Broadcom Control Suite 2.
Start BACS2. Click the tab on Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 2 that provides the information of interest or from which to perform a desired test, diagnostic, analysis, or set adapter properties.
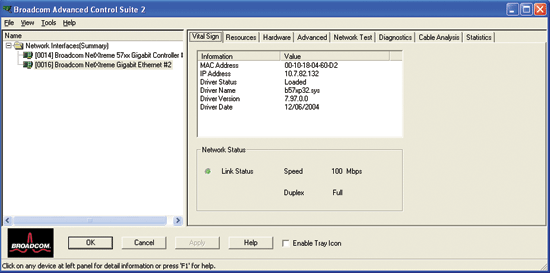
The Vital Sign tab shows useful information about the Broadcom NetXtreme Gigabit Ethernet adapter in your computer. Such information includes the link status of the adapter and network connectivity.
 |
MAC Address. This is a physical MAC (media access control) address that is assigned to the adapter by the manufacturer. The physical address is never all 0s.
IP Address: The network address that is associated with the adapter. If the IP address is all 0s, this means that the associated driver has not been bound with Internet Protocol (IP).
Driver Status. The status of the adapter driver.
Loaded. Normal operating mode. The adapter driver has been loaded by Windows and is functioning.
Not Loaded
Information Not Available
Driver Name/Version/Date. The file name, version, and creation date of the software driver that is associated with the adapter.
Network Status: The following network status information is provided:
Link Status. The indicator is green if a link is established. A red indicator means that a link is not established.
Speed. The link speed of the adapter.
Duplex. The duplex mode in which the adapter is operating.
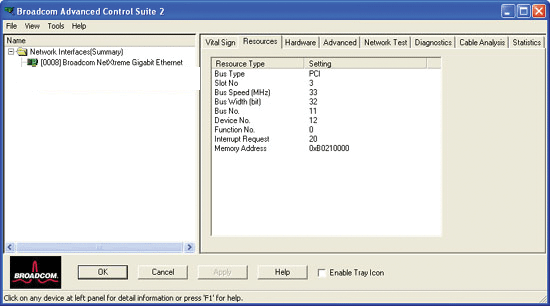 |
Bus Type. The type of input/output (I/O) interconnect used by the adapter.
Slot No. The slot number on the system board occupied by the adapter. Depending on BIOS support, this item may or may not be available for PCI Exress™ type add-in NIC adapters. This item is not available for PCI Express type LOM adapters.
Bus Speed (MHz). The bus clock signal frequency used by the adapter. This item is not available for PCI-E type adapters.
Bus Width (bit). The number of bits that the bus can transfer at a single time to and from the adapter. This item is not available for PCI Express™ type adapters.
Bus No. Indicates the number of the bus in which the adapter is installed.
Device No. The number assigned to the adapter by the operating system.
Function No. The port number of the adapter. For a single-port adapter, the function number is 0.
Interrupt Request. The interrupt line number that is associated with the adapter. Valid numbers range from 2 to 25.
Memory Address. The memory mapped address that is assigned to the adapter. This value can never be 0.
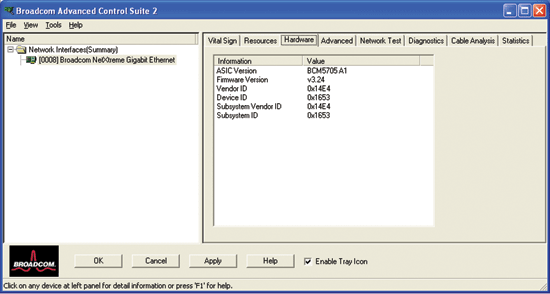 |
ASIC Version. The chip version of the Broadcom adapter (this information is not available for adapters made by others).
Firmware Version. The firmware version of the Broadcom adapter (this information is not available for adapter made by others).
Vendor ID. The vendor ID.
Device ID. The adapter ID.
Subsystem Vendor ID. The subsystem vendor ID.
Subsystem ID. The subsystem ID.
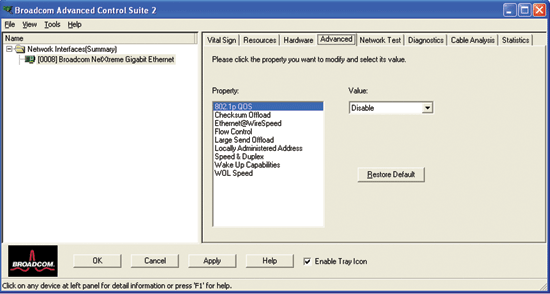 |
From the Advanced tab, you can view and change the values of the available properties of the selected adapter. The potentially available properties and their respective settings are described below. To view the value of a property, click the name of the property in the Property list. The property value is displayed in the Value box. To change the value, click an item in the Value list or type a new value, as appropriate (selection options are different for different properties).
NOTES:
|
The 802.1p QOS property enables quality of service, which is an Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IEEE) specification that treats different types of network traffic differently to ensure required levels or reliability and latency according to the type of traffic. This property is disabled by default. Unless the network infrastructure supports QoS, do not enable QoS. Otherwise, problems may occur.
Normally the Checksum Offload function is computed by the protocol stack. When you select one of the Checksum Offload property values (other than None), the checksum can be computed by the network adapter.
Rx TCP/IP Checksum. Enables receive TCP, IP, and UDP checksum offloading.
Tx TCP/IP Checksum. Enables transmit TCP, IP, and UDP checksum offloading.
TX/Rx TCP/IP Checksum (default). Enables transmit and receive TCP, IP, and UDP checksum offloading.
None. Disables checksum offloading.
The Ethernet@Wirespeed property enables a Gigabit Ethernet adapter to establish a link at a lower speed when only 2 pairs of wires are available in the cabling plant. By default, this property is set to Enable. To disable Ethernet@Wirespeed, change the setting to Disable.
Disable. Disables Ethernet@Wirespeed.
Enable (default). Enables Ethernet@Wirespeed.
The Flow Control property enables or disables the receipt or transmission of PAUSE frames. PAUSE frames enable the network adapter and a switch to control the transmit rate. The side that is receiving the PAUSE frame momentarily stops transmitting.
Auto (default). PAUSE frame receipt and transmission are optimized.
Disable. PAUSE frame receipt and transmission are disabled.
Rx PAUSE. PAUSE frame receipt is enabled.
Rx/Tx PAUSE. PAUSE frame receipt and transmission are enabled.
Tx PAUSE. PAUSE frame transmission is enabled.
The Jumbo Mtu property allows the network adapter to transmit and receive oversized Ethernet frames that are greater than 1514 bytes, but less than 9000 bytes in length. This property requires the presence of a switch that is able to process Jumbo frames.
Frame size is set at 1500 bytes by default. To increase the size of the received frames, increment the byte quantity in 500-byte increments.
Normally the TCP segmentation is done by the protocol stack. When you enable the Large Send Offload property, the TCP segmentation can be done by the network adapter.
Disable. Disables Large Send Offload.
Enable. (default). Enables Large Send Offload.
The Locally Administered Address is a user-defined MAC address that is used in place of the MAC address originally assigned to the network adapter. Every adapter in the network must have its own unique MAC address. This locally administered address consists of a 12-digit hexadecimal number.
Value. Assigns a unique node address for the adapter.
Not Present (Default). Uses the factory-assigned node address on the adapter.
The appropriate assigned ranges and exceptions for the locally administered address include the following:
The Speed & Duplex property sets the connection speed and mode to that of the network. Note that Full-Duplex mode allows the adapter to transmit and receive network data simultaneously.
10 Mb Full. Sets the speed at 10 Mbit/s and the mode to Full-Duplex.
10 Mb Half. Sets the speed at 10 Mbit/s and the mode to Half-Duplex.
100 Mb Full. Sets the speed at 100 Mbit/s and the mode to Full-Duplex.
100 Mb Half. Sets the speed at 100 Mbit/s and the mode to Half-Duplex.
Auto (default). Sets the speed and mode for optimum network connection (recommended).
| |
NOTES
|
The Wake Up Capabilities property enables the network adapter to wake up from a low-power mode when it receives a network wake-up frame. Two types of wake-up frames are possible: Magic Packet™ and Wake Up Frame.
Both (default). Selects both Magic Packet and Wake Up Frame as wake-up frames.
Magic Packet. Selects Magic Packet as the wake-up frame.
None. Selects no wake-up frame.
Wake Up Frame. Selects Wake Up Frame as the wake-up frame and allows the network adapter to wake the system when an event such as a ping or an Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) request is received.
The WOL Speed property sets the speed at which the network adapter connects to the network while the network adapter is in Wake on LAN mode. By default, the WOL Speed property is set to Auto.
10 Mb. Sets the speed to 10 Mbit/s. This is the network speed when the system is in a standby mode awaiting a wake-up frame.
100 Mb. Sets the speed to 100 Mbit/s.
Auto (default). Sets the speed for optimum network connection.
From the Network Test tab, you can verify IP network connectivity. This test verifies if the driver is installed correctly and tests connectivity to a gateway or other specified IP address on the same subnet. Network Test uses TCP/IP. The network test sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets to remote systems and waits for a response. If a gateway is configured, the test automatically sends packets to that system. If a gateway is not configured or if the gateway is unreachable, the test prompts you for a destination IP address.
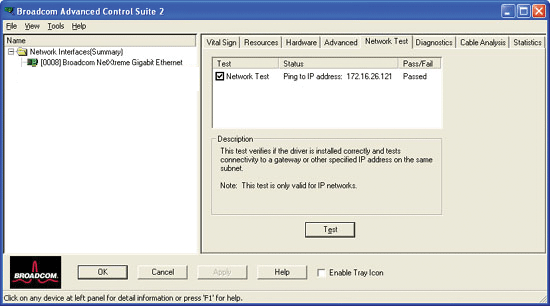 |
From the Diagnostics tab, you can perform diagnostic tests only on the physical components of Broadcom network adapters. The tests are continuously performed on the selected physical components. The number of passes and fails in the Pass/Fail column increments each time the tests are performed. For example, if a test is performed four times and there are no fails, the value in the Pass/Fail column is 4/0. If there were 3 passes and 1 fail, however, the value in the Pass/Fail column is 3/1.
| |
NOTE: The network connection is temporarily lost when these tests are running. |
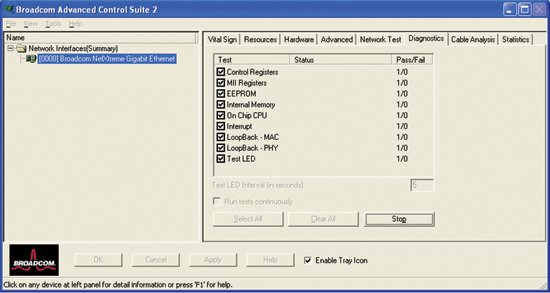 |
Control Registers. This test verifies the read and write capabilities of the network adapter registers by writing various values to the registers and verifying the results. The adapter driver uses these registers to perform network functions such as sending and receiving information. If the test fails, the adapter may not be working properly.
MII Registers. This test verifies the read and write capabilities of the registers of the physical layer (PHY). The physical layer is used to control the electrical signals on the wire and for configuring network speeds such as 1000 Mbit/s.
EEPROM. This test verifies the content of the electrically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM) by reading a portion of the EEPROM and computing the checksum. The test fails if the computed checksum is different from the checksum stored in the EEPROM. An EEPROM image upgrade does not require a code change for this test.
Internal Memory. This test verifies that the internal memory of the adapter is functioning properly. The test writes patterned values to the memory and reads back the results. The test fails if an erroneous value is read back. The adapter cannot function without its internal memory.
On-Chip CPU. This test verifies the operation of the internal CPUs in the adapter.
Interrupt. This test verifies that the Network Device Driver Interface Specification (NDIS) driver is able to receive interrupts from the adapter.
Loopback MAC and Loopback PHY. These tests verify that the NDIS driver is able to send packets to and receive packets from the adapter.
Test LED. This test causes all of the port LEDs to blink 5 times for the purpose of identifying an adapter when multiple adapters are installed.
From the Cable Analysis tab, you can run a test to determine if you have the appropriate length of cable connected. The Cable Length test makes this determination by using a return loss algorithm. This information allows you to determine whether a problem you may be experiencing is related to the adapter or if the cabling is too long.
| |
NOTES:
|
To run a Cable Length test
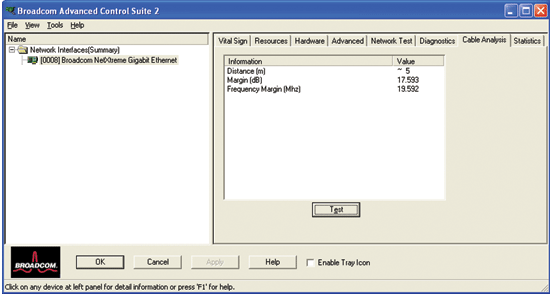 |
The resulting test information is described below:
Distance. The estimated cable length in meters (an average of all 4 channels using a return loss algorithm).
Margin. The minimum difference (in dB) between the measured length of the cable pair and the maximum length specified in IEEE 802.3ab.
Frequency Margin. The minimum difference (in MHz) between the measured frequency of the cable pair and the maximum frequency specified in IEEE 802.3ab.
From the Statistics tab, you can view traffic statistics for the both Broadcom adapters and adapters made by others. Statistical information and coverage are more comprehensive for Broadcom adapters.
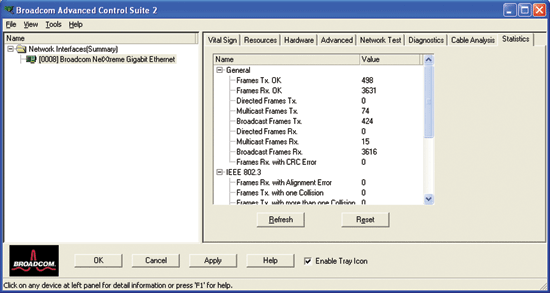 |
Frames Tx OK. A count of frames that are successfully transmitted. This counter is incremented when the transmit status is reported as Transmit OK.
Frames Rx OK. A count of frames that are successfully received (Receive OK). This does not include frames received with frame-too-long, frame check sequence (FCS), length or alignment errors, or frames lost due to internal MAC sublayer errors. This counter is incremented when the receive status is reported as Receive OK.
Directed Frames Tx. A count of directed data frames that are successfully transmitted.
Multicast Frames Tx. A count of frames that are successfully transmitted (as indicated by the status value Transmit OK) to a group destination address other than a broadcast address.
Broadcast Frames Tx. A count of frames that were successfully transmitted (as indicated by the transmit status Transmit OK) to the broadcast address. Frames transmitted to multicast addresses are not broadcast frames and therefore, are excluded.
Directed Frames Rx. A count of directed data frames that are successfully received.
Multicast Frames Rx. A count of frames that are successfully received and are directed to an active nonbroadcast group address. This does not include frames received with frame-too-long, FCS, length or alignment errors, or frames lost due to internal MAC sublayer errors. This counter is incremented as indicated by the Receive OK status.
Broadcast Frames Rx. A count of frames that are successfully received and are directed to a broadcast group address. This count does not include frames received with frame-too-long, FCS, length or alignment errors, or frames lost due to internal MAC sublayer errors. This counter is incremented as indicated by the Receive OK status.
Frames Rx with CRC Error. The number of frames received with CRC errors.
Frames Rx with Alignment Error. A count of frames that are not an integral number of octets in length and do not pass the FCS check. This counter is incremented when the receive status is reported as Alignment Error.
Frames Tx with one Collision. A count of frames that are involved in a single collision and are subsequently transmitted successfully. This counter is incremented when the result of a transmission is reported as Transmit OK, and the attempt value is 2.
Frames Tx with more than one Collision. A count of frames that are involved in more than one collision and are subsequently transmitted successfully. This counter is incremented when the transmit status is reported as Transmit OK, and the value of the attempts variable is greater than 2 and less or equal to the attempt limit.
Frames Tx after Deferral. A count of frames whose transmission was delayed on the first attempt because the medium was busy. The frames involved in any collision are not counted.
| |
NOTE: Custom statistics are available only for an enabled Broadcom NetXtreme Gigabit Ethernet adapter. |
Frames size less than 64-byte with bad FCS. The number of frames with a size less than 64 bytes with bad FCS.
MAC Rx w/ Pause Command and Length = 0. MAC control frames with the pause command and a length equal to 0.
MAC Rx w/ Pause Command and Length greater than 0. MAC control frames with the pause command and a length greater than 0.
MAC Rx w/ no Pause Command. MAC control frames with no pause command.
MAC Sent X-on. MAC Transmit with X-on was on.
MAC Sent X-off. MAC Transmit with X-on was off.
Large Send Offload Transmit Requests. The number of times the NIC was requested to transmit a packet performing TCP segmentation.
The Configuration tab is available only on mobile platforms. From the Configuration tab, you can set the NIC Battery Saving Mode option. When the NIC Battery Saving Mode option is selected, the computer is on battery power and link auto-negotiation is reversed, linking at the lowest speed possible, thereby prolonging the life of the battery.